We should all be thinking about saving for retirement — and there are many ways to go about it.
When comparing a pension to a 401(k), it’s essential to understand how each option works and what it offers. Both have unique benefits that can shape your retirement strategy. By evaluating the features of both, you’ll be better equipped to choose the one — or a combination — that fits your financial goals and provides long-term security.
What is a pension plan?
A pension plan is a retirement program funded and managed by your employer. It promises a specific income upon retirement, usually based on your salary and years of service.
This traditional option provides stability and predictability, making it easier to plan for your future without worrying much about investment decisions or market risks.
How pension plans work
Pension plans are built on a defined benefit model, where your employer guarantees a fixed retirement payment. The amount you receive is typically based on factors like your average salary and how long you've worked for the company.
For example, a plan may offer 1.5% of your average salary over your last five years of employment multiplied by the number of years you've worked. The longer you stay with the company, the higher your benefits will be.
Your employer funds and manages the pension, which means they handle all investment decisions. Since they bear the investment risk, you don't have to worry about market fluctuations affecting your retirement income, but you also don’t have any control over their decisions.
Pension plans also often include vesting schedules, which determine when you fully own your pension benefits.
For instance, you might need to work for five years before becoming fully vested. If you leave the company before reaching that point, you could lose some or all of your pension benefits, so it’s important to understand the vesting schedule before making career decisions.
Types of pension plans
There are two main types of pension plans:
Defined benefit plans: These are the traditional pensions where the employer guarantees a set retirement benefit based on salary and years of service. This ensures a predictable income stream during retirement.
Defined contribution plans: This includes options like cash balance plans and involve contributions from both you and your employer. The benefit depends on the contributions and how the investments perform. While you may face more investment risk, higher returns are also potential.
Hybrid plans: There is also the option to combine elements of both. For example, a cash balance plan credits your account with a percentage of your salary plus interest. These plans aim to offer more predictability than traditional defined contribution plans while giving you more flexibility than traditional pensions.
What is a 401(k) plan?
A 401(k) is a retirement savings account that lets you contribute part of your paycheck before income taxes are taken out. The money is invested in options like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, allowing you to grow your savings.
How 401(k) plans work
With a 401(k), you decide how much of your salary you want to contribute, up to the IRS limits. Since the contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, they lower your annual taxable income.
Many employers also offer matching contributions — for example, they might match 50% of your contributions, up to 6% of your salary. In this case, the employer's contribution and your own will steadily grow to be used in the future.
You choose how to invest your 401(k) funds from a selection of options provided by your plan. These options often include mutual funds, stocks, and bonds, each with different levels of risk and return.
Your 401(k) growth will depend on your contributions and how well your investments perform.
Types of 401(k) plans
There are several types of 401(k) plans, each with its own features:
Traditional 401(k): Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income today. You’ll pay taxes when you withdraw the funds in retirement.
Roth 401(k): Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, so you don’t get a tax break now. However, qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, including any investment earnings. This is beneficial if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket when you retire.
Safe Harbor 401(k): This plan is designed to simplify administration for employers. They must make fully vested contributions immediately, which can encourage employee participation. It also helps employers avoid certain IRS tests.
Simple 401(k): Ideal for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees, this plan combines features of traditional 401(k)s and Simple IRAs. Employers must contribute, and employees are immediately vested. It reduces administrative burdens, making it easier for small businesses to offer retirement benefits.
Key differences between pensions and 401(k)s
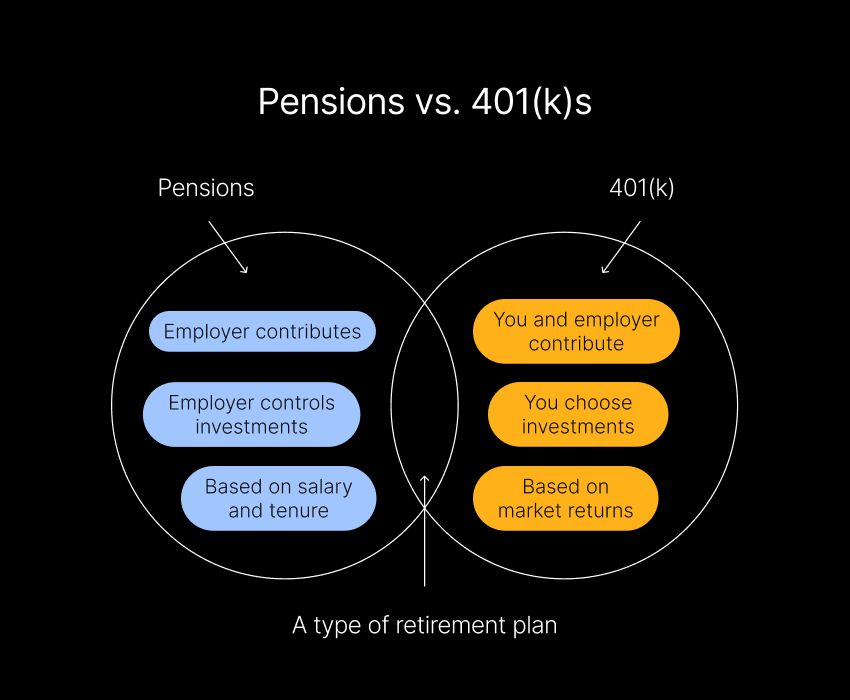
When comparing a pension plan to a 401(k), there are several key differences in how they work, the level of control they offer, and the risks involved. All of these are important to know to make a smart decision for your goals.
Contributions and funding
In a pension plan, your employer primarily funds your retirement benefit. They contribute to the pension fund and manage the investments. Depending on the plan, you may not need to contribute at all. This makes things simple, but it also means you have less control over how much is saved for your retirement.
With a 401(k), you decide how much of your salary to contribute, up to IRS limits. While many employers offer matching contributions, they’re not guaranteed. Here, you have more control over your savings, but you're also responsible for making sure you're contributing enough to meet your retirement goals.
Risk and security
Pension plans offer more security because your employer guarantees a specific benefit amount. They assume the investment risk so that market fluctuations won’t affect your retirement income. However, this stability depends on your employer’s financial health. If the company faces financial trouble, your pension benefits could be at risk, although there are usually protections in place.
In a 401(k), you bear the investment risk. The value of your retirement account is tied to the performance of your chosen investments. Market downturns can decrease your balance, which impacts your retirement savings. While this adds some risk, it also offers the potential for higher returns if your investments perform well. You’re in control but must stay on top of your investment strategy.
Flexibility and control
A 401(k) gives you more flexibility and control. You decide how much to contribute, choose your investments, and can change your strategy as needed. If you change jobs, you can roll over your 401(k) from your previous employer into your new 401k plan or an IRA without facing any tax penalties.
Pension plans generally provide less flexibility. You typically have no control over contributions or investment decisions. The benefits are based on a predetermined formula, and there are limited options for portability. If you leave your employer before becoming fully vested, you might also lose some or all of your pension benefits.
Pros and cons of pension plans
Understanding the pros and cons of pension plans will help you decide if they’re a good fit for your retirement strategy.
Pros
Guaranteed income: Pensions provide predictable retirement income, making planning and budgeting easier.
Employer-funded: Your employer handles funding and investments, so you don’t need to worry about contributing or managing investments.
Financial security: Since the employer takes on the investment risk, the idea is that your benefits stay stable even if the market fluctuates.
Benefits for long-term employees: The longer you stay with the company, the higher your pension benefits may be.
Cons
Lack of portability: Pensions are tied to your employer, making it hard to transfer benefits if you change jobs.
Limited control: You don’t have control over how pension funds are invested or managed.
Employer dependency: If your employer faces financial trouble, your pension benefits could be at risk.
Vesting requirements: You may lose some or all of your benefits if you leave the company before becoming fully vested.
Pros and cons of 401(k) plans
You’ll also need to weigh the pros and cons of 401(k) plans to decide if this savings method fits your retirement goals.
Pros
Control over contributions and investments: You decide how much to save and where to invest.
Tax advantages: Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income. Your investments grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
Employer matching: Many employers offer matching contributions, boosting your savings.
Portability: If you change jobs, you can roll over your 401(k) to a new employer’s plan or an IRA.
Cons
Investment risk: You're responsible for investment decisions; poor performance can impact your savings.
Fees: Administrative and management fees can eat into your returns over time.
Contribution limits: There are annual limits on how much you can contribute, which may limit how much you can save.
Early withdrawal penalties: Withdrawing before age 59½ may result in taxes and penalties.
How to choose between a pension and a 401(k)
Choosing between a pension and a 401(k) depends on your personal financial goals, employment situation, and how comfortable you are with managing investment risk.
Evaluate your financial goals
Think about what you want your retirement to look like. A pension might be the better fit if you value guaranteed income and don’t want to worry about managing investments. Its predictability can provide peace of mind.
On the other hand, if you’re comfortable making investment decisions and are open to the potential for higher returns, a 401(k) could be right for you. The flexibility to choose your investments and adjust your savings approach will give you more control to tailor your retirement to your goals.
Factors like your desired retirement age, expected expenses, and plans for leaving an inheritance should guide your decision.
For assistance with your planning, a financial app like Albert can offer various features to help you assess your financial goals and stay on track with your retirement goals, so you don’t have to navigate the decision alone.
Considering your employment situation
Your choice may also depend on what your employer offers. If you have access to a pension and a 401(k), using both can give you a balanced retirement plan. The pension provides a guaranteed income, while the 401(k) offers the potential for growth and flexibility.
A pension plan could be a solid option if you plan to stay with your employer for the long haul. But if you expect to change jobs or careers, the portability of a 401(k) might suit you better.
Look closely at your job stability, career plans, and employer’s retirement offerings. The right plan for you depends on your specific situation.
Making the right retirement choice for you
Choosing between a pension and a 401(k) is an important decision that will shape your financial future. Pensions offer guaranteed income and security, but they come with less flexibility. On the other hand, 401(k)s give you control over your savings and the growth potential, but they come with investment risk and require you to stay on top of your portfolio.
To make the best choice, evaluate your financial goals with the help of a budgeting app like Albert and think about your current and future employment situation. In some cases, it’s possible to participate in both plans, giving you a balanced retirement approach.
Planning ahead and staying informed helps you build a retirement strategy that meets your needs. Whether you're considering a pension, a 401(k), or both, understanding your options will allow you to make a decision that brings you financial security and peace of mind.
⚡️ Download Albert today and start planning for your future.
